Find out how you can leverage entities for your website SEO.
Search engines have evolved; they have come a long way since introduced decades ago. Gone are the days when you stuff keywords into your content and pray that your page would rank. Google, in particular, has become a sophisticated learning machine that is now learning how to analyze how we use our language to provide us with better search results.
With the advent of entities, there is a drastic change in our understanding of search engine optimization. No longer are we confined in just using keywords; we are now more focusing on entity SEO.
What’s entity-based SEO?
How relevant is this, and how can we use this to optimize content?
We are going to answer all these questions and some more in this post. We’ve provided you with comprehensive information about entities, why they are essential, and how you can utilize this for your SEO for entity search campaigns.
What Does an Entity Mean?
An entity is a noun, be it a tangible concept, or otherwise. This concept, by Google definition, is anything from “a thing to a concept that is singular, unique, well defined and distinguishable.”
An entity is not just the innate meaning of a particular word. It’s also the association we contextually correlate to that specific word. Each entity has attributes that provide more meaning to the entity. For example, your dog can have a breed, color, age, name, etc.
Here are some takeaways about entities
- Each entity has a unique ID.
- Each entity represents a real object or concept.
- Entities are connected with other entities.
- Google determines what entity to use in the knowledge panel by the frequency of that entity appearing on the top 10 ranked sites. The higher the frequency, the more likely it is to be added to the panel.
- Entities are stored in a database, which contains more than 500 million entities.
- You rank entities using a scoring system.
- There are contextual methods used when entities contain the same names.
- Google can learn new entities.
- Entities are language-agnostic.
Importance of Entities to SEO
You might be wondering why Google changed the way things are or what is an entity in SEO. The answer is straightforward. Our devices have evolved, too. We become more mobile and use Google more than before.
There is also a correlation between semantic search using entities and unstructured data. Google is about machine learning nowadays. What Google is doing now is answering your queries right on the search page results instead of directing you to a website where you can hopefully figure out the answers.
Entities are the game-changer for SEO now. They answer the issue of unstructured data or a type of data that had no classification in a pre-determined setting. For years, this type of information caused ambiguities such as difficulty in finding patterns for data retrieval, or if search engines indeed had found some structure, they could not provide meaning to such information.
Using entities solves these issues as the data was labeled individually as an entity, so there is easier data processing compared with in the past. Structured data provided by entities aren’t only crawlable and indexable; search engines would be able to understand user intent more and can process more substantial chunks of data to provide users with more reliable answers.
Besides, paid search is becoming lucrative. Instead of spending hundreds to thousands of cash, companies seek to improve their organic searches. Another point to contend is that Google is shifting gears from a keyword-laden, long content to a more in-depth discernment of what the words meant.
How Entities Changed SEO
While in the past, SEO is all about the proper use of keywords; nowadays, there is more emphasis on how your SEO can develop connections and provide answers now.
- Enhanced mobile research
Entities made research much more available conveniently regardless you are using your desktop or mobile gadget. Moreso, entities paved the way for Google to give more to mobile-first indexing.
- No more translations
Entities surpass the need to translate for words in a different language. Translations are an attribute already.
- Rich snippets
For your content to rank higher on SERPs, it should be featured as a snippet; it should answer commonly used questions by users for that particular topic. With chunks of information placed in a structured manner, search engines can use the data in your content for the featured snippets, making your post more visible to users.
How Do Entities Work?
Entities share attributes with other entities. Say, we are using an entity on dogs. The entity calls out the attributes or characteristics of dogs. Examples of such would be dogs are mammals, the different types of breeds, color, and the likes.
Since attributes are shareable, dogs share the attribute “mammal” with other animals we consider mammals. Similarly, a dachshund shares the attribute “breed” with a golden retriever.
That said, you can connect entities as long as the attributes are related. If this is just a mere keyword search, the results would include scattered ideas that contain that particular keyword.
Also, entities allow co-occurrence wherein Google can distinguish what to list when the entity represents two or more entirely different concepts. For example, the word Ritz. This word can be a luxury hotel chain, a surname, or a food brand. Using your search history and a guessed search intent, Google shows one of those three answers. It would focus on that single result based on the factors mentioned above.
Say, the result returns as The Ritz-Carlton Hotel. The search results would not just focus on The Ritz alone. Google would also mention related words that pertain to The Ritz-Carlton and hotels in general. It would include competitors of The Ritz-Carlton, famous personalities such as Coco Chanel and places such as London.
If you associate such a concept to the pages, all the essential words in your content are considered entities. Each entity connects to another to create a relationship. Put the entity in a larger picture; then, you can deduce that a web page can be an entity and establishes a connection with another through links. By this, we are talking about larger entities (the pages) containing smaller entities (the words).
Entities vs. Keywords
Before search engines used entities, SEO is about putting as many keywords and their variations in the content as possible. The goal is to be on top with little emphasis on the quality of content. But when Google introduced the Knowledge Graph, among others, keywords have taken a backseat in place of entities.
Take note, though, you can’t eliminate keywords altogether; these are still interrelated with entities. You can find all the top information about an entity in that box as in the case of the entity dog. Check the image below.
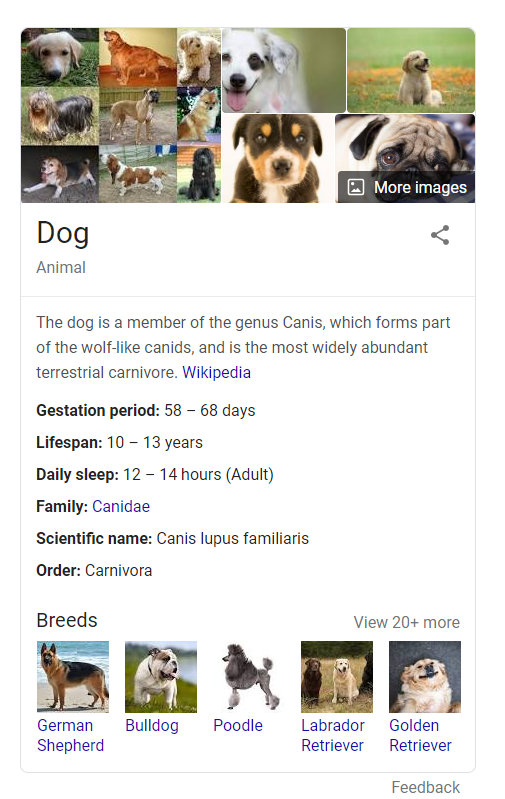
Google Entity SEO
You use keywords to narrow down choices as well as provide clues for a particular answer. These are not exactly the answers per se people are looking for. That’s why SEO specialists take a great deal of time in optimizing the keywords so readers can better see them.
While the importance of keywords may have dimmed down these past few years, it’s not yet time for keywords to die. They are your keys to enable Google to identify your content as entities.
On the other hand, you don’t really search for entities, but you want to learn more about that particular entity. Let’s go back to our example, dogs. You already know about dogs. That’s why you’re putting that word in the search box, to begin with. But you want a deeper understanding of dogs, for example, dog breeds for the elderly. Basically, you are seeking information about that entity.
The results for this query would be about the types of dogs suitable for the elderly. However, if entities are not involved, the query results would most likely end up having definitions of a dog or websites about dogs in general. Also, if you look at the People Also Ask section, you’d find questions like the best pet for an elderly woman or the best dog breed for an elderly woman.
With entities, Google is trying to fill in the gaps of what we might want to have as answers. As mentioned in the previous section, entities are ideas with shareable attributes and are easily accessible to everyone via Google’s Knowledge Graph. Entities don’t follow any specific language, either.
How Do Search Engines Use Entities?
You might wonder what is an entity in SEO. The Knowledge Graph is an entity that contains all other entities related to that information. If you’re not considered as an entity, you don’t belong in that said graph. Hence, you won’t come up as an answer to a query. First and foremost, Google must acknowledge you as an entity. Then, you and other related entities are grouped to form topics. Next, these topics are used for relevant pages and searches. Entities are also factors that determine the relevance of particular content.
It is still unknown how entities exactly play into search results. Nevertheless, if we check researches, entities take into account relatedness or how strong the connection of the entities is to one another, whether on a webpage or in general.
The relationship strengths of two or more entities are defined by the following:
- Frequency of entities being combined together
- The authoritative power of the webpage or blog
Are Entities a Ranking Factor?
Absolutely. Early testing results show entities have a strong affinity as a ranking factor—also, there two distinct ranking factors influenced by entities.
- Links
To be on top of the search engine results in entity-based indexing, you need links from authentic and authoritative sites.
- Content
Keywords and content, well, they co-exist. Keywords determine how relevant and valuable your content is. If you want Google to notice your content in its entity-based indexing, there should be a strong connection between those keywords to signal Google your content is high-value.
Four Factors Used for Ranking Entities
Here are the four major factors Google uses for ranking entities.
1. How related the entity is to other entities
This refers to the frequency of entities being referenced together in a query. If the entities are often used together or referenced with one another, they could be pulled into a single result.
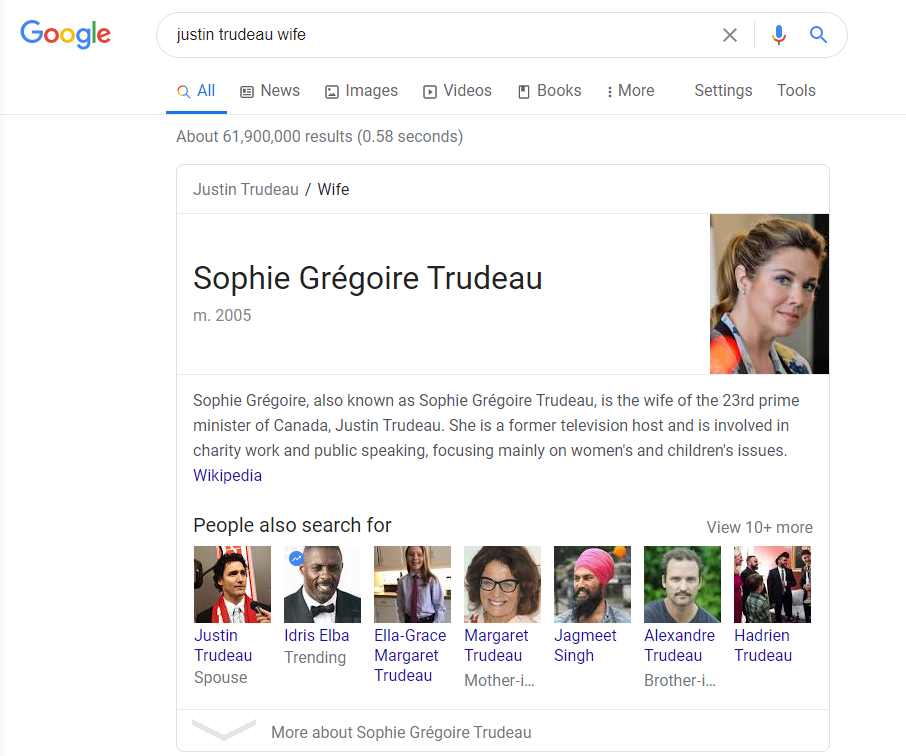
For example, if two entities, Justin Trudeau and Canada, are added to the search box, it would yield the current Prime Minister of Canada. Why? Because these two entities are often associated with one another.
But try changing Canada to wife and Google would show you PM Justin Trudeau’s wife, Sophie.
What’s the implication of this? Google is not just showing you the top results for your main keyword but the top results of the two entities as to how they are correlated in your query or text.
2. How notable the entity is
This refers to how prominent the entity is with the category where it is competing. That said, an entity would have an increase in notability when the category is small, and the entity has a high value. Relevance, links, and reviews determine value.
3. How much contribution the entity provides
This refers to the amount of contribution the entity provides for the category it is ranking.
4. Are there prizes the entity has received?
When the entity receives a legitimate award, its value also increases.
How Long Have Entities Been Used in Algorithms
“Things. Not Strings.”
Entities have been present for quite a long time, but it was only when Google first rolled out the mobile-first indexing that entities have taken the limelight. One thing is for sure. More possibilities are popping up because of entities. Google now can identify the distinction between words so it can give users a more relevant result.
How to Optimize Content for Entities
There’s one thing you must remember- a surefire way to be ahead of the game is by making sure your content would answer your audience’s needs. The better you are at it, the more that search engines would recognize your content.
Before we dive into the nuances of entities and content, remember that the scope of entities far-reaching and well beyond content. Also, there is no denying that content and entities basically have to work together.
Pick a topic and do thorough research.
Look for a topic. Your keyphrase is vital. For your content to rank using your keyphrase, you should analyze and gather data on the related subjects and ideas. Basically, you are preempting what Google might think as significant in its entity graph.
Where to find pertinent information related to your keyword
- Wikipedia
Majority of Google’s entities are in Wikipedia
- Google Images
Under the search bar are words inside a bubble. Some may not be attributes of your keyword but Google associates these words to your keyword like the image below:
- People Also Ask
This contains related topics and questions that Google links to your keywords. We did one on entity SEO as an example:
Analyze Your Competition using the NLP API
Find the top three ranking articles for your keyword. Run them through an entity extraction tool to better discern what entities are being used more often. Look for the salience score. The higher it is, the more important your keyword is to the entire content. Choose the ones that have higher scores.
Regularly update your content.
This enables you to keep track of which related topics are trending.
Use relevant entities
But never overstuff your content with entities. You have to make sure the entities are referenced and related to the topic.
Look for intent
Whenever you want a page to rank, you must determine the intent Google is trying to convey. You need to check the SERPs for this one. Make sure that Google understands your keyword so it can better understand your content.
You can check out the top ten ranking pages. Compare how your target keywords fare with that of your competitors. Use a keyword analyzer for this. Adding your location can further narrow down your needed keywords.
Don’t forget to analyze the search volume of those keywords starting a year ago. Copy and use the keywords that have the highest associations as Google considers them entities. This way, your content becomes more relevant and easily understood by search engines.
Create expert content
Create micro websites with a few pages that tackle a single topic. Put them in sub-directories as opposed to the common practice of putting them on sub-domains. This way, Google can distinguish these pages as part of the domain and brand. A concise, library-like organization of your single-topic content tells Google that you have a lot of information on this. Hence, you should be considered an expert on that said topic.
Make your content easy to understand
An easily digestible content with simple words, structured headlines, headings, lists, and the likes is what Google prefers. Create a structured content wherein Google understands the headings, the titles, and the different paragraphs. You have to make sure that cohesion exists between these elements.
Don’t use weak CTRs
Check your past content for weak click-through rates. If you found some, make sure that you optimize the section where those were found.
Summary
Entities and entity SEO is the future. You must orient yourself about these concepts as these can help you moving forward. Do you need help with your website’s SEO? Give us a call or contact ITDwebdesign.com so our experienced and professional SEO experts discuss what we can do for you.










Leave A Comment